This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution that helps you learn core concepts. Question: an If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and the quantity demanded for Product F to increase by 17%, what is the cross-price elasticity of demand?
Explaining the impact of Sales Price, Volume, Mix and Quantity Variances on Profit Margin (Current year vs Last Year) – Learn Accounting Finance
You use our calculator in the “decrease X by Y” mode, or you can calculate it manually by plugging the numbers into the second formula above to get $100 – $100 x 30 / 100 = $100 – $100 x 0.3 = $100 – $30 = $70 final price after decreasing it by the percent off.

Source Image: synder.com
Download Image
If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and… Question: If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity

Source Image: junglescout.com
Download Image
7 Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand Business Economics If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and the quantity demanded for Product F to increase by 17%, what is the cross-price elasticity of demand? Round your answer to one decimal place.

Source Image: shopify.com
Download Image
If The Price Of Product E Decreasing By 2
Business Economics If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and the quantity demanded for Product F to increase by 17%, what is the cross-price elasticity of demand? Round your answer to one decimal place. Answer & Explanation Solved by verified expert Answered by nickybairagi21 The cross-price elasticity of demand between Product E and Product F is −8.5. Given the negative value of the cross-price elasticity, Products E and F are complements. Step-by-step explanation Let’s break this down step by step: Cross-price elasticity of demand (XED):
5 Best Discount Strategies + Examples (2022)
Step 1 Identify variables % change in price of Product E = –2% (decrease) % change in quantity demanded of Product E = 14% % change in quantity demanded of Product F = 17%. Step 2 – Formula Cross Price Elasticity of demand = % change in quantity demanded for Product A / % change in price of product B. Step 3 – Computation 32 Customer Experience Statistics for 2024
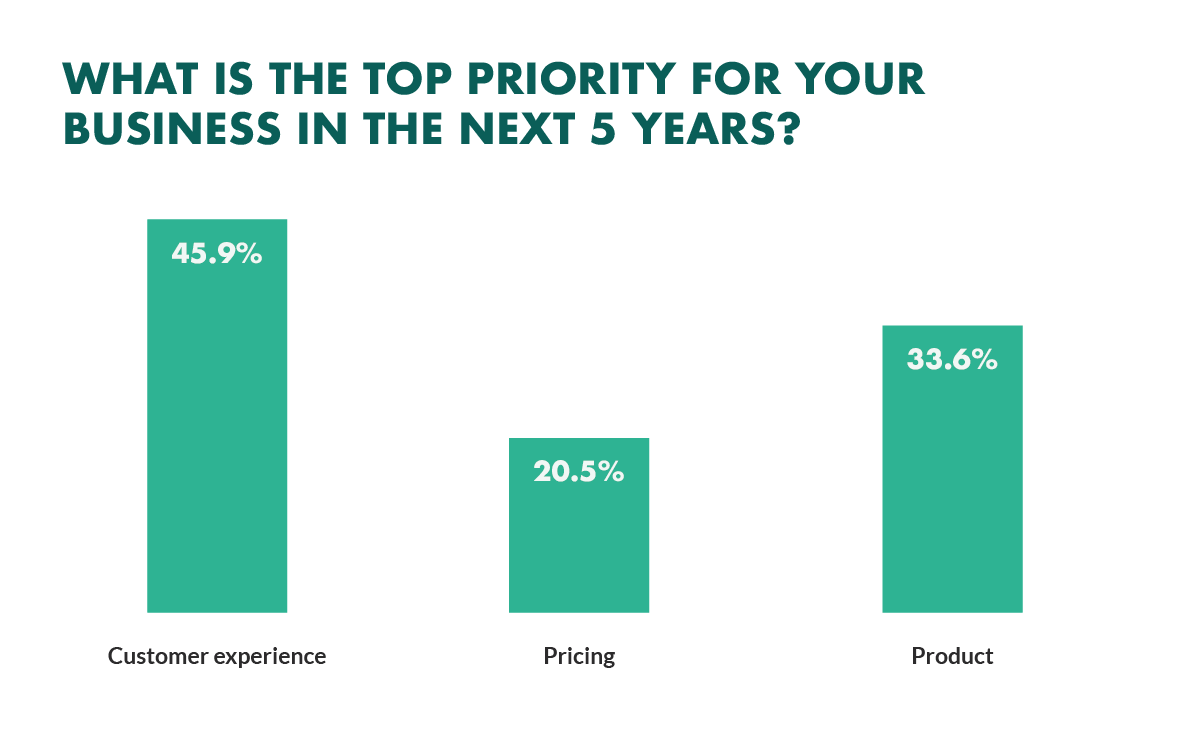
Source Image: superoffice.com
Download Image
Economics of Software Part 2: Elasticity Explained – Mind the Product Step 1 Identify variables % change in price of Product E = –2% (decrease) % change in quantity demanded of Product E = 14% % change in quantity demanded of Product F = 17%. Step 2 – Formula Cross Price Elasticity of demand = % change in quantity demanded for Product A / % change in price of product B. Step 3 – Computation
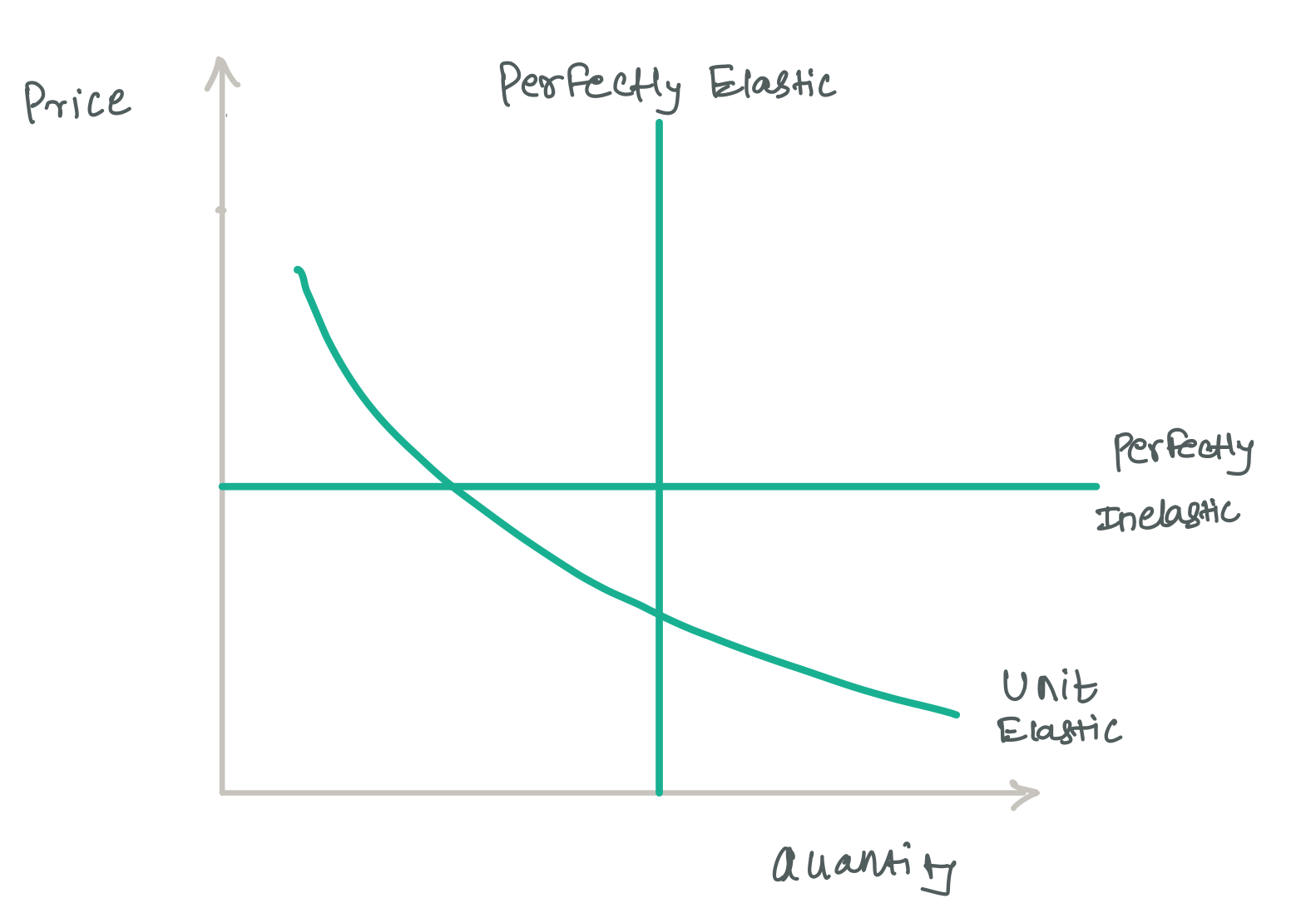
Source Image: mindtheproduct.com
Download Image
Explaining the impact of Sales Price, Volume, Mix and Quantity Variances on Profit Margin (Current year vs Last Year) – Learn Accounting Finance This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution that helps you learn core concepts. Question: an If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and the quantity demanded for Product F to increase by 17%, what is the cross-price elasticity of demand?

Source Image: learnaccountingfinance.com
Download Image
7 Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and… Question: If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity

Source Image: symson.com
Download Image
10 User Persona Examples for SaaS Products and How to Create Them Next, we take the results of our calculations and plug them into the formula for price elasticity of supply: Price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. Again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to
Source Image: userpilot.com
Download Image
Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC): What Is It, and How Is It Calculated? Business Economics If the price of Product E decreasing by 2% causes its quantity demanded to increase by 14% and the quantity demanded for Product F to increase by 17%, what is the cross-price elasticity of demand? Round your answer to one decimal place.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Cashconversioncycle-f39bee15fd174aae897c72466b2449ff.jpg)
Source Image: investopedia.com
Download Image
How Much Do Facebook Ads Cost? (2023 Benchmarks) Answer & Explanation Solved by verified expert Answered by nickybairagi21 The cross-price elasticity of demand between Product E and Product F is −8.5. Given the negative value of the cross-price elasticity, Products E and F are complements. Step-by-step explanation Let’s break this down step by step: Cross-price elasticity of demand (XED):
Source Image: blog.hootsuite.com
Download Image
Economics of Software Part 2: Elasticity Explained – Mind the Product
How Much Do Facebook Ads Cost? (2023 Benchmarks) You use our calculator in the “decrease X by Y” mode, or you can calculate it manually by plugging the numbers into the second formula above to get $100 – $100 x 30 / 100 = $100 – $100 x 0.3 = $100 – $30 = $70 final price after decreasing it by the percent off.
7 Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC): What Is It, and How Is It Calculated? Next, we take the results of our calculations and plug them into the formula for price elasticity of supply: Price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. Again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to